In the pursuit of thriving plants, the right fertilizer can make all the difference. Among various options, Potassium Nitrate Fertilizer stands out for its effectiveness. This nutrient-rich compound provides plants with both potassium and nitrogen. These elements are essential for growth and vitality.
When considering the best Potassium Nitrate Fertilizer for 2026, one must think beyond standard choices. It's important to look for quality products that deliver consistent results. Many farmers and gardeners have found that not all fertilizers perform equally. Some may lead to uneven growth or even harm delicate plants.
However, long-term use of any fertilizer can also have drawbacks. It’s crucial to monitor soil health and nutrient levels. Over-reliance on Potassium Nitrate Fertilizer can lead to imbalances. Balancing nutrients ensures plants remain healthy and productive. A thoughtful approach often yields robust plants and bountiful harvests.

Potassium nitrate is a key ingredient in many fertilizers. It contains essential nutrients, primarily potassium and nitrogen. These elements support plant growth, enhancing root development and boosting overall health. According to agricultural studies, potassium nitrate can improve crop yield by up to 25% under optimal conditions.
Plants benefit significantly from potassium nitrate. Nitrogen promotes vegetative growth, while potassium strengthens cell walls and improves drought resistance. When applying potassium nitrate, the timing matters. Over-application can lead to nutrient imbalances. Many growers lack this knowledge, which can lead to poor plant performance.
Soil tests are crucial before using any fertilizer. Regular testing ensures proper nutrient levels and avoids over-fertilization. Some studies indicate that growers often underestimate the importance of balanced nutrition. They may focus on one nutrient, neglecting others that support plant health. This creates cycles of growth that are not sustainable. Reflecting on these issues can guide better practices in the future.
Potassium nitrate fertilizers have gained attention for promoting healthy plant growth. In 2026, the market offers diverse options tailored for various agricultural needs. Common types include granular, liquid, and slow-release formulations. Each type presents unique advantages. Granular fertilizers provide long-lasting nutrient release. Liquid options allow quick absorption. Slow-release formulations ensure a steady supply over time.
In recent reports, 45% of farmers prefer granular types for their versatility. They can be mixed into the soil easily. Many consider them user-friendly. However, liquid fertilizers are becoming popular. They often lead to quicker visible results. The demand for liquid potassium nitrate has increased by 30% recently. This shift indicates changing preferences in agriculture.
Each type has pros and cons. Granular fertilizers may not dissolve swiftly, which could delay nutrient availability. Liquid options may require more frequent applications. Therefore, understanding specific needs is crucial. Farmers must reflect on their soil composition and plant requirements. A tailored approach often yields the best results. Balancing time and effort may prove challenging but rewarding in nutritional management.
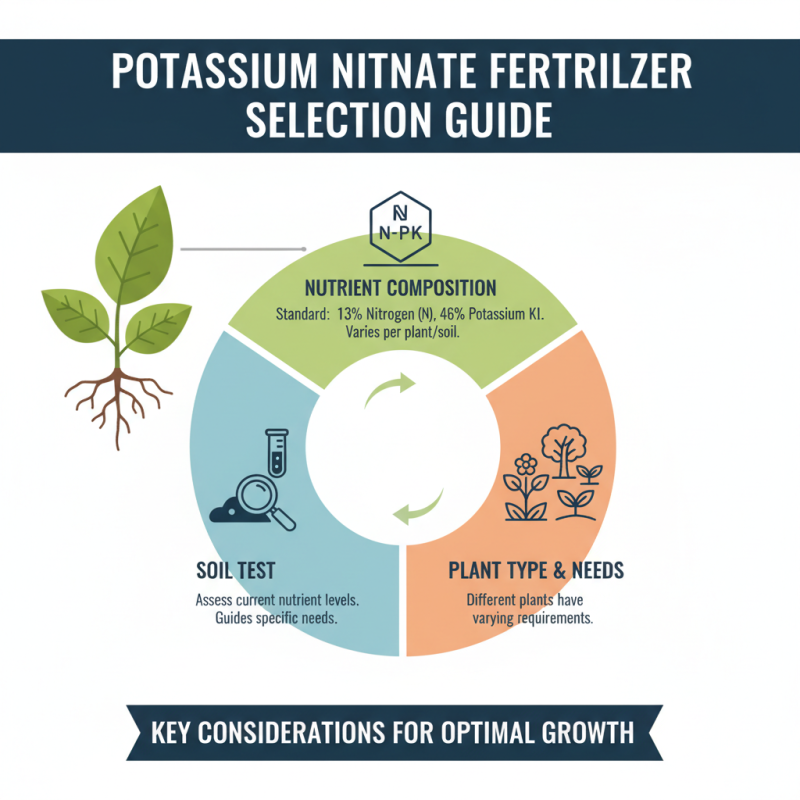
When selecting potassium nitrate fertilizers, several factors should be considered. The nutrient composition is crucial. Standard potassium nitrate typically contains around 13% nitrogen and 46% potassium. However, specific needs may vary based on plant types and soil quality. Conducting a soil test helps to assess nutrient levels, guiding your fertilizer choice.
Application rates are another important factor. Over-application can harm plants, while under-application often leads to nutrient deficiencies. Studies suggest that optimal potassium levels can increase crop yield by 10-15%. However, applying too much can result in salt buildup in the soil, damaging root systems.
Additionally, consider the granule size and solubility of the fertilizer. Smaller granules often dissolve quickly, providing immediate access to plants. However, slower-release options can sustain nutrients over time. Think about the long-term effects on your soil health. Remember, the right fertilizer is not just about immediate results, but also about maintaining soil fertility for future plantings. Finding the right balance can be tricky and requires ongoing experimentation and adjustment.
Applying potassium nitrate effectively can greatly enhance your gardening success. However, it's crucial to understand the recommended methods for application. One common technique is to dissolve potassium nitrate in water. This creates a nutrient-rich solution that can be easily absorbed by plants. Use about one to two tablespoons per gallon of water for a balanced mix. Watering with this solution ensures that nutrients reach the roots directly.
In addition to soil application, foliar feeding is another efficient method. Spray the potassium nitrate solution directly onto the leaves. This allows plants to take in nutrients quickly. Early morning is the best time to spray, reducing evaporation. Yet, caution is needed; too much can lead to leaf burn. It's essential to monitor your plants and adjust accordingly.
Most gardeners make mistakes in the amount they apply. Overuse can harm the environment and the plants. Thus, it's important to perform soil tests. This helps to determine existing nutrient levels. Ideally, fertilizers should complement what the soil already contains. Experimenting with small quantities can prevent potential disasters. Getting it right takes time and practice.
This chart illustrates the recommended application rates of potassium nitrate for various types of plants, showcasing the optimal amounts for achieving healthy growth. The data reflects the average application rates for different plant categories, measured in grams per square meter.
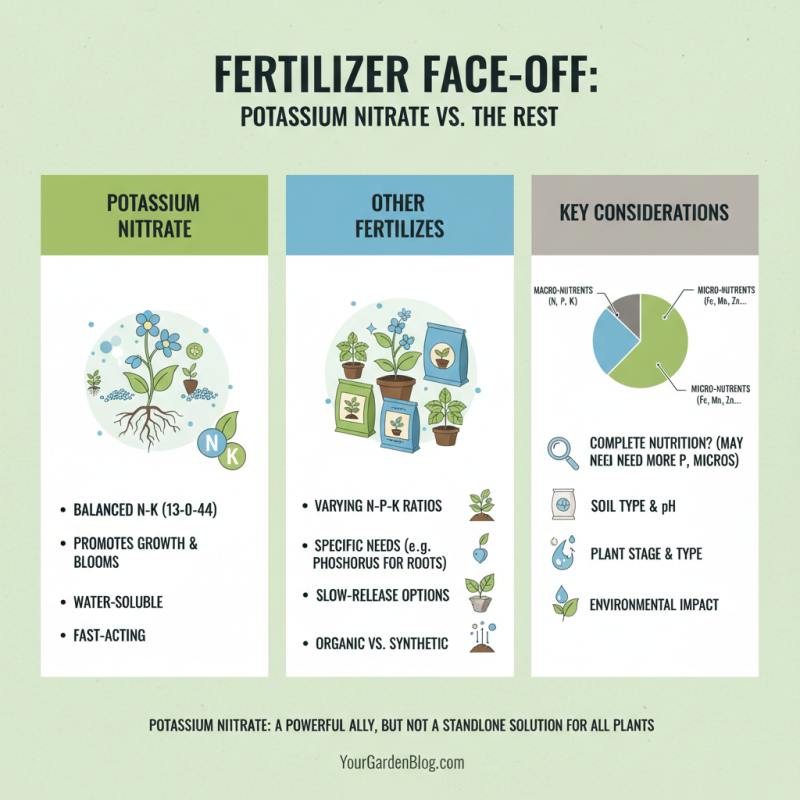
Potassium nitrate is a popular choice for plant health, but how does it stack up against other fertilizers? Many gardeners favor it for its balanced nutrient profile. It delivers vital nitrogen and potassium, essential for growth and flowering. However, relying solely on potassium nitrate may not address all plant needs.
In comparison with organic options, potassium nitrate acts quickly. Organic fertilizers release nutrients more slowly, which can be beneficial. Some plants thrive on this gradual feed. Potassium nitrate might lead to rapid growth, but that can stress the plant. It's important to monitor plant response closely. A plant may look lush one week and wilt the next.
Additionally, some gardeners may find themselves in a routine: adding the same fertilizers year after year. This could lead to nutrient imbalances in the soil. It's crucial to test soil health regularly. The inappropriate application of potassium nitrate can also burn plants. Reflection is necessary to identify the right balance. Each garden is unique, and what works for one might not work for another. Take time to understand your plants’ needs.