Potassium Nitrate Powder is a versatile chemical with many applications. This compound is often used in fertilizers, food preservation, and fireworks. Its ability to provide essential nutrients makes it vital in agriculture. Farmers frequently rely on Potassium Nitrate Powder to enhance crop yield and quality.
In addition to agriculture, Potassium Nitrate Powder is significant in the food industry. It serves as a preservative, helping to prolong shelf life. This aspect raises questions about its safety and usage. Some people may worry about its effects on health. However, when used properly, it is considered safe.
Moreover, Potassium Nitrate Powder has a place in pyrotechnics. It creates vibrant colors and impressive effects in fireworks. Yet, improper handling can lead to accidents. It highlights the need for responsible use. Understanding the benefits and potential risks of Potassium Nitrate Powder is essential. Through informed choices, users can maximize its benefits while minimizing issues.
Potassium nitrate powder is a chemical compound with the formula KNO3. It consists of potassium, nitrogen, and oxygen. Its white, granular texture makes it easy to handle and use. This compound is not only important in agriculture but also serves various other purposes.
In agriculture, potassium nitrate is a vital source of potassium and nitrogen for plants. It enhances crop yields and is often found in fertilizers. Reports indicate that its usage can increase yield by 10% or more in certain crops. Beyond its agricultural applications, potassium nitrate is used in food preservation. It helps in curing meats, preventing bacteria growth, and enhancing color. However, there are drawbacks to consider. Overuse in fertilizers can lead to soil nutrient imbalance.
Potassium nitrate also finds applications in the production of fireworks and explosives. It acts as an oxidizer, providing necessary oxygen for combustion. This can be a double-edged sword; while it enables creativity in design, it poses safety risks. Recent data indicates that improper handling has led to increased accidents in manufacturing environments. Awareness is crucial. Understanding how to use potassium nitrate safely will benefit both industries and consumers.
Potassium nitrate, a chemical compound with the formula KNO₃, has unique properties. It appears as a white crystalline powder. This compound is highly soluble in water, creating a clear solution. The prismatic crystals can sometimes be mistaken for table salt. Its hygroscopic nature allows it to absorb moisture from the air.
In agriculture, potassium nitrate serves multiple purposes. It is often used as a fertilizer, providing essential nutrients to plants. The compound supplies both potassium and nitrogen, helping crops thrive. However, excessive use in soil can lead to nutrient imbalance. Farmers need to manage its application carefully.
Beyond agriculture, potassium nitrate finds use in various industries. It is employed in food preservation and even in certain fireworks. Interestingly, its explosive potential has raised concerns over safety. Careful handling and proper regulations are needed. Balancing its benefits with risks is crucial in its application.
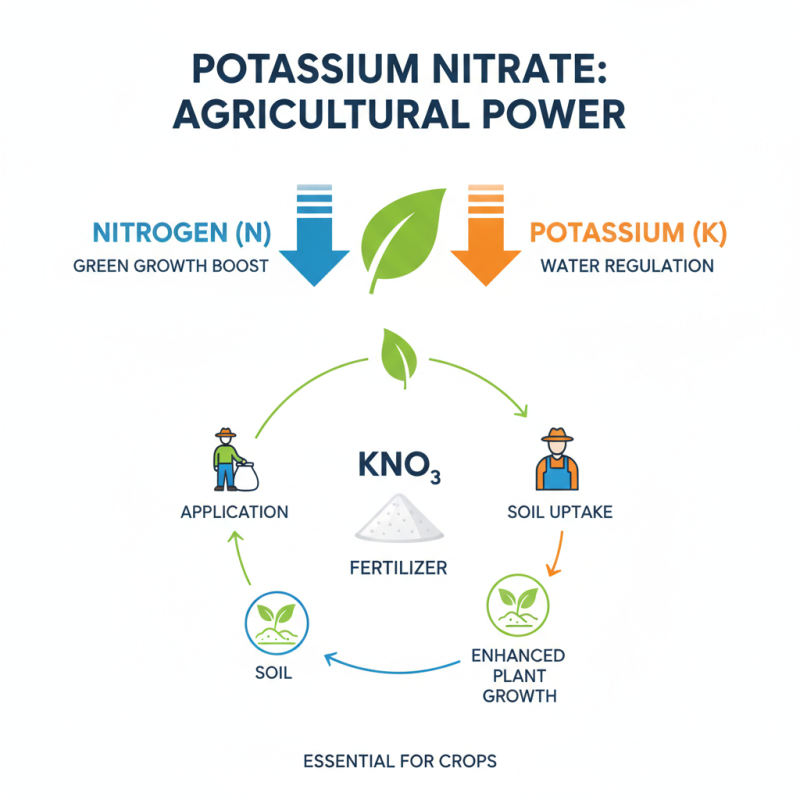
Potassium nitrate powder, often recognized for its diverse applications, plays a vital role in agriculture. Farmers frequently use it as a fertilizer due to its high nitrogen and potassium content. Both elements are essential for plant growth. Potassium supports water regulation in plants, while nitrogen boosts green growth.
In crop production, potassium nitrate improves yield and quality. It enhances fruit size and flavor. This compound is especially beneficial for leafy greens and root vegetables. Its easy solubility means it quickly enters the soil. But, improper use can lead to nutrient imbalance. Farmers sometimes overlook the specific needs of their crops.
Irrigation practices can also affect the efficacy of potassium nitrate. Over-application might cause leaf burn or hinder growth. Therefore, careful monitoring is necessary. Understanding soil composition can help in applying the right amount. Experiences can vary, and it's essential to learn from each season. Adjusting application methods is a continual process.
Potassium Nitrate Powder is widely used in food preservation. This compound helps inhibit spoilage. It prevents the growth of harmful bacteria. As a result, it extends the shelf life of various foods. Common foods that benefit from this include meats and dairy products. By using potassium nitrate, manufacturers can ensure food safety. However, consumers need to be aware of its usage.
While beneficial, there are concerns about the health effects of potassium nitrate. Some studies suggest possible risks if consumed in large amounts. It might have implications for certain individuals. Therefore, moderation is crucial. Always read labels to understand its presence in foods. This awareness can help make informed choices.
In culinary practices, balancing safety and flavor is key. Potassium nitrate enhances taste but may raise questions about its necessity. Some chefs explore natural alternatives for preservation. They seek options that are less controversial. The conversation around potassium nitrate continues as food safety evolves. This calls for a critical reflection on its role in our diets.
Potassium nitrate, also known as saltpeter, plays a vital role in various industries. According to recent industry reports, the global potassium nitrate market is expected to grow substantially, reaching over $1 billion by 2027. This demand is driven largely by its applications in fertilizers and food preservation.
In manufacturing, potassium nitrate is crucial. It is commonly used in pyrotechnics and as a heat agent in chemical reactions. The compound helps produce flames and smoke in fireworks. In the food industry, it acts as a preservative, enhancing shelf life and preventing bacterial growth. However, some concerns about nitrates in food intake persist. These worries indicate the potential need for more stringent regulations.
Additionally, potassium nitrate is instrumental in the glass and ceramics industries. It aids in controlling viscosity and improving the quality of the final product. Despite its benefits, manufacturers must ensure the usage aligns with safety standards. Continuous evaluations are necessary to maintain balance between effectiveness and safety in these applications.






